Smoothing of EBSD Data
Discusses how to smooth and to fill missing values in EBSD data
Smoothing a single grain
Let's start out analysis by considering a single magnesium grain
% import standard data set mtexdata twins % compute grains [grains,ebsd.grainId,ebsd.mis2mean] = calcGrains(ebsd,'angle',10*degree); % restrict data to one single grain [~,id] = max(grains.area); oneGrain = grains(id); ebsd = ebsd(oneGrain); plot(ebsd,ebsd.orientations) hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'micronbar','off') hold off
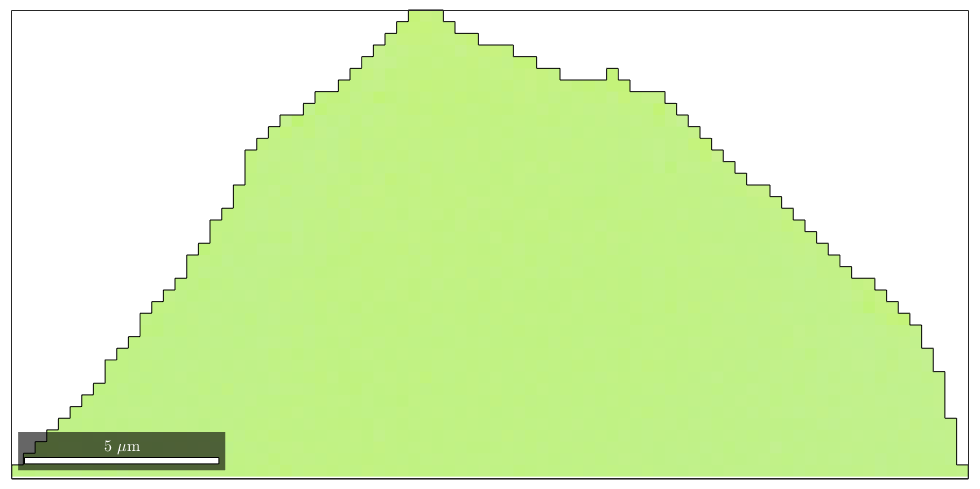
With the default colormap, we can not distinguish any orientation gradient within the grain. Let's adapt the colormap to this specific grain
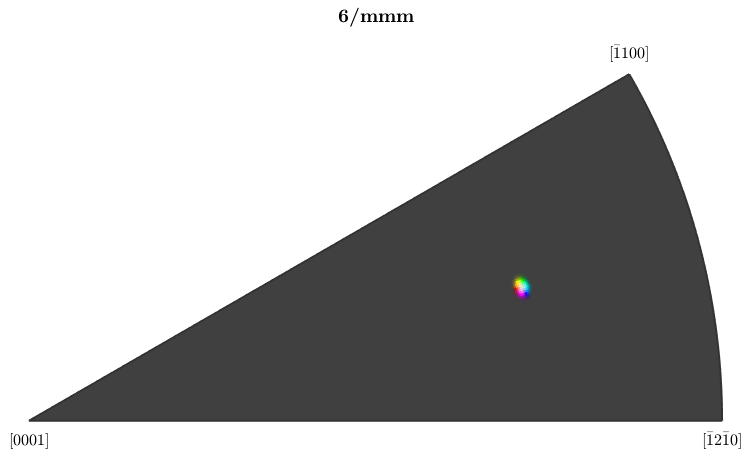
ipfKey = ipfHSVKey(ebsd); % set inversePoleFigureDirection such that the mean orientation is % colorized white ipfKey.inversePoleFigureDirection = grains(id).meanOrientation * ipfKey.whiteCenter; % concentrate the colors around the mean orientation ipfKey.maxAngle = 1.5*degree; % plot the colormap plot(ipfKey,'resolution',0.25*degree)
Warning: Possibly applying an orientation to an object in specimen coordinates!
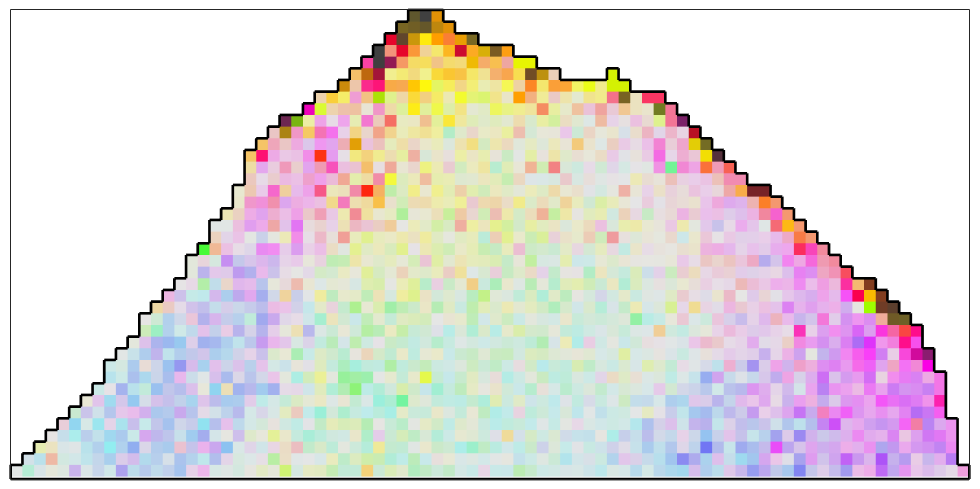
With the new colormap, we can clearly see the noise overlapping the texture gradient within the grain.
% plot the grain plot(ebsd,ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd.orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off
The Mean Filter
The simplest filter to apply to the orientation data is the meanFilter which simply takes the mean of all orientations within a certain neighborhood.
% define the meanFilter F = meanFilter; % smooth the data ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd,F); % plot the smoothed data plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),... ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off
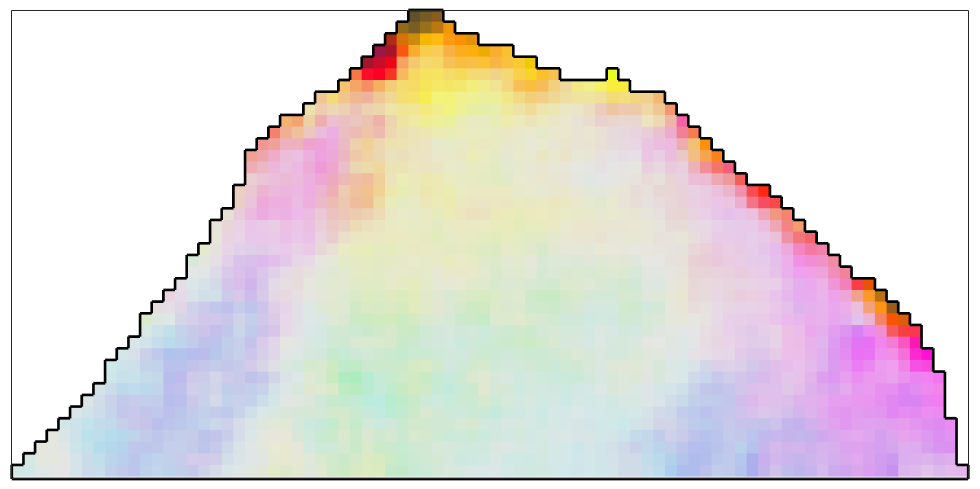
As an additional option, one can specify the size of the neighborhood and weights for the averaging. Let's define a 5x5 window with weights coming from the Gaussian distribution.
[x,y] = meshgrid(-2:2); F.weights = exp(-(x.^2+y.^2)/10); % smooth the data ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd,F) % plot the smoothed data plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),... ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off
ebsd_smoothed = EBSD
Phase Orientations Mineral Color Symmetry Crystal reference frame
0 1264 (39%) notIndexed
1 2016 (61%) Magnesium light blue 6/mmm X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
Properties: bands, bc, bs, error, mad, x, y, grainId, mis2mean
Scan unit : um
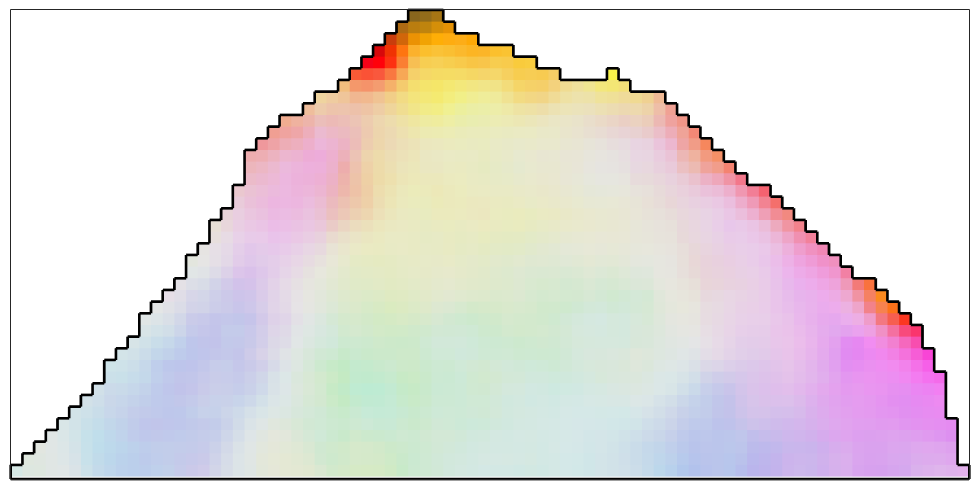
The Median Filter
The disadvantage of the mean filter is that is smoothes away all subgrain boundaries and is quite sensitive against outliers. A more robust filter which also preserves subgrain boundaries is the median filter
F = medianFilter; % define the size of the window to be used for finding the median F.numNeighbours = 3; % this corresponds to a 7x7 window % smooth the data ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd,F); % plot the smoothed data plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),... ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off
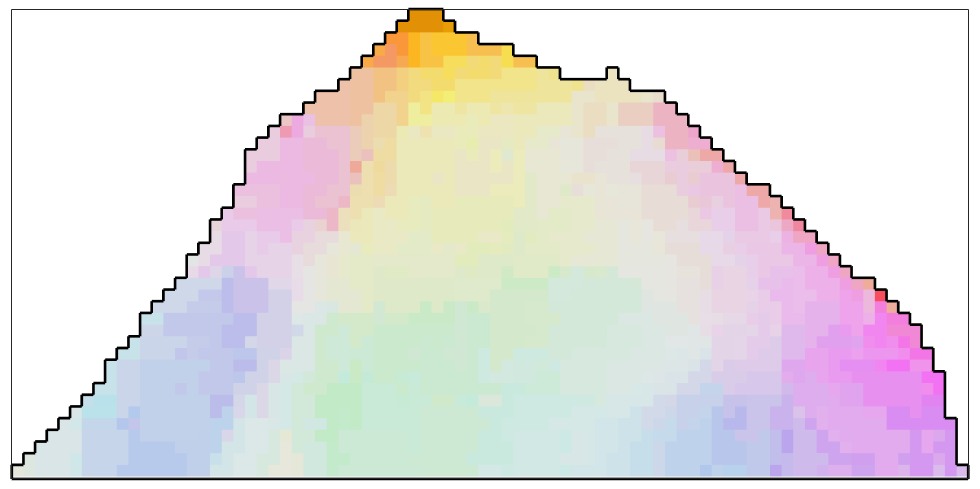
The Kuwahara Filer
F = KuwaharaFilter; F.numNeighbours = 5; % smooth the data ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd,F); % plot the smoothed data plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),... ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off
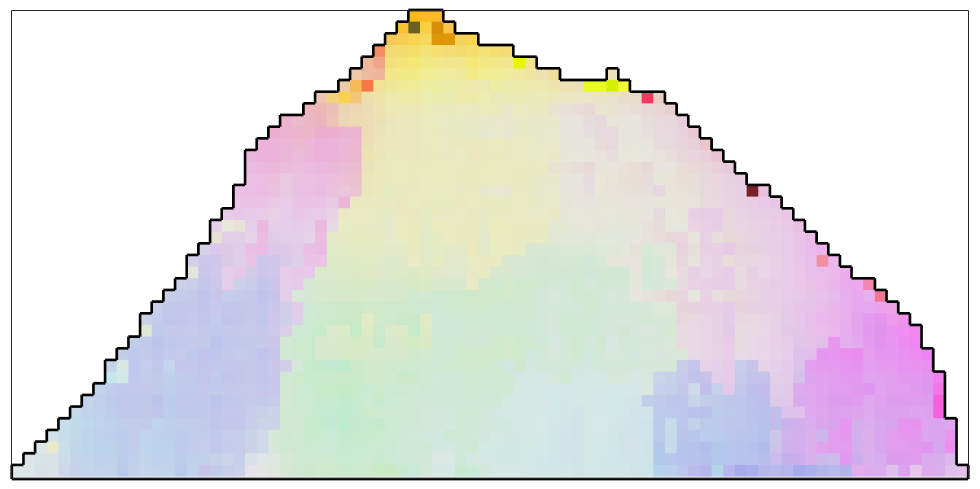
The Smoothing Spline Filter
The smoothing spline filter is up to now the only filter that automatically calibrates the smoothing parameter
F = splineFilter; % smooth the data ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd,F); % plot the smoothed data plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),... ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off % the smoothing parameter determined during smoothing is F.alpha
ans =
4.6123
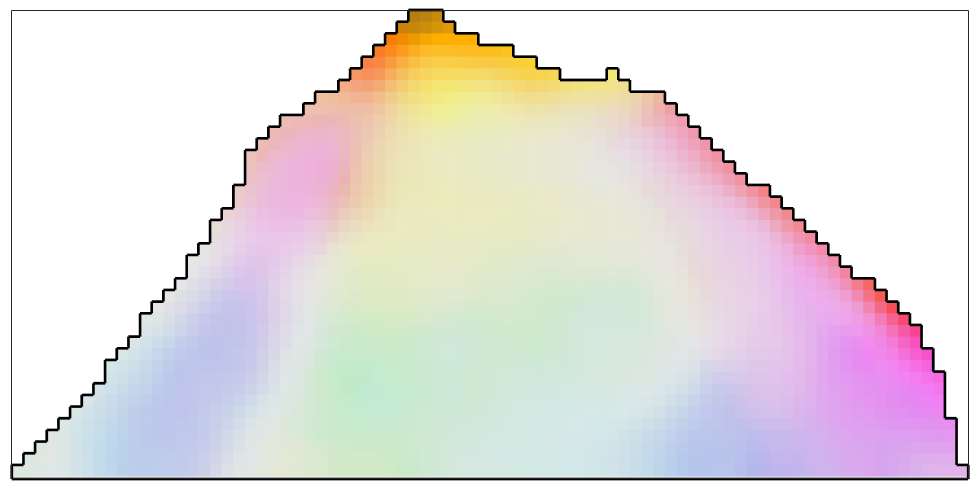
The halfquadratic Filter
The halfquadratic filter differs from the smoothing spline filter by the fact that it better preserves inner grain boundaries. We will see this in a later example.
F = halfQuadraticFilter; F.alpha = 0.25; %set the smoothing parameter % smooth the data ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd,F); % plot the smoothed data plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),... ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off
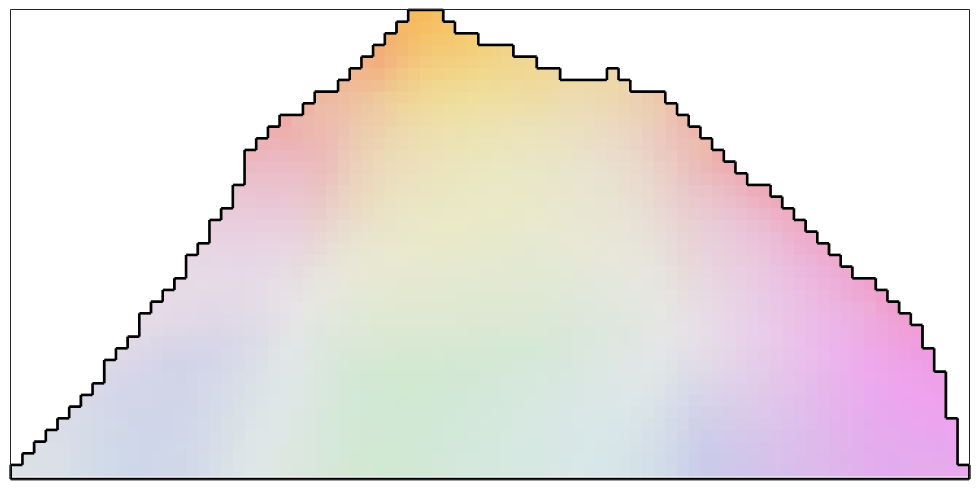
The Infimal Convolution Filter
The infimal convolution filter differs from the smoothing spline filter by the fact that it better preserves inner grain boundaries. We will see this in a later example.
F = infimalConvolutionFilter; F.lambda = 0.01; %smoothing parameter for the gradient F.mu = 0.005;% smoothing parameter for the hessian % smooth the data ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd,F); % plot the smoothed data plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),... ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations),'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off

Interpolating Missing Data
The filters above can also be used to interpolate missindexed orientations.
A synthetic example
In the following example, we randomly set 50 percent of the measured orientations to nan.
ebsdNaN = ebsd; % set 50 percent of the orientations to nan ind = discretesample(length(ebsd),round(length(ebsd)*50/100)); ebsdNaN(ind).orientations = orientation.nan(ebsd.CS); % plot the reduced data plot(ebsdNaN,ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsdNaN.orientations)) hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary,'micronbar','off') hold off
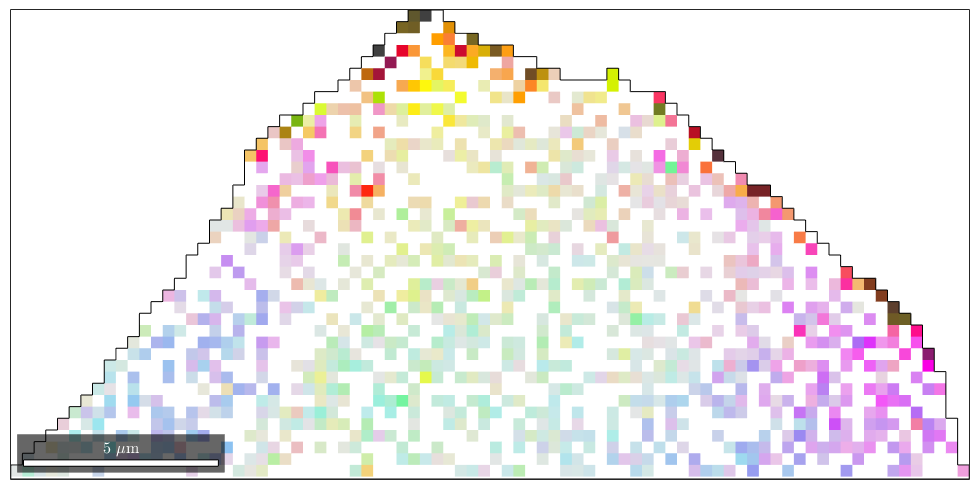
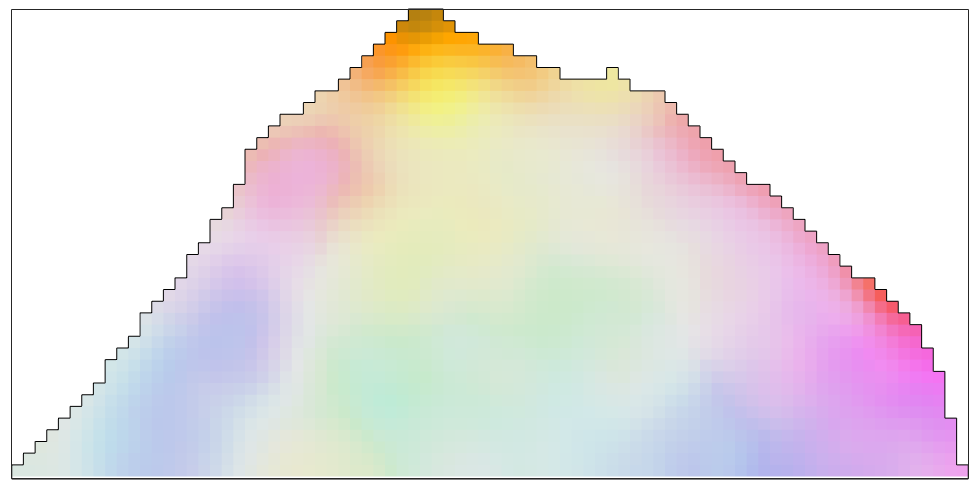
By default, all orientations that are set to nan are interpolated.
% interpolate the missing data with the smoothing spline filter ebsdNaN_smoothed = smooth(ebsdNaN,splineFilter); color = ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsdNaN_smoothed('indexed').orientations); plot(ebsdNaN_smoothed('indexed'),color,'micronbar','off') hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary) hold off
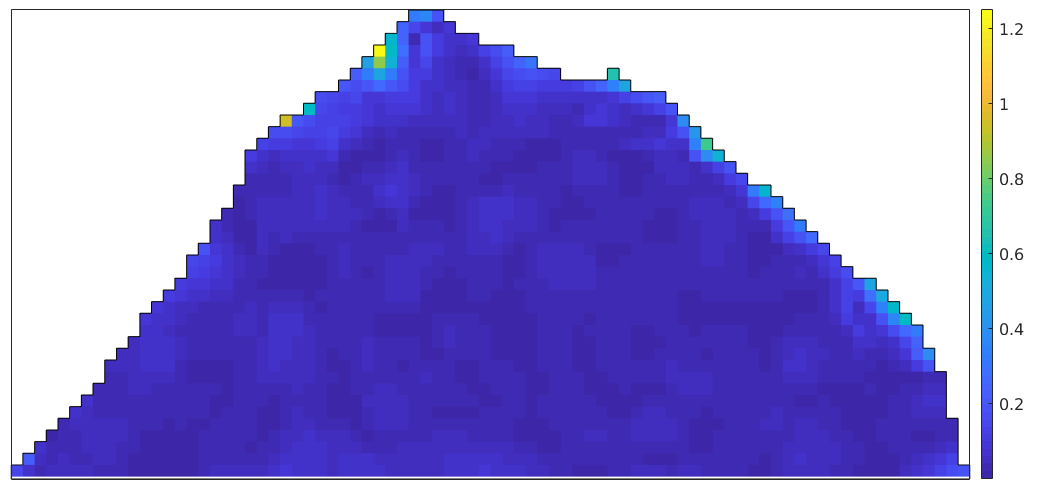
We may plot the misorientation angle between the interpolated orientations and the measured orientations
omega = angle(ebsdNaN_smoothed('indexed').orientations, ... ebsd_smoothed('indexed').orientations); plot(ebsd_smoothed('indexed'),omega./degree,'micronbar','off') mtexColorbar hold on plot(oneGrain.boundary) hold off
A real world example
Let's consider a subset of the
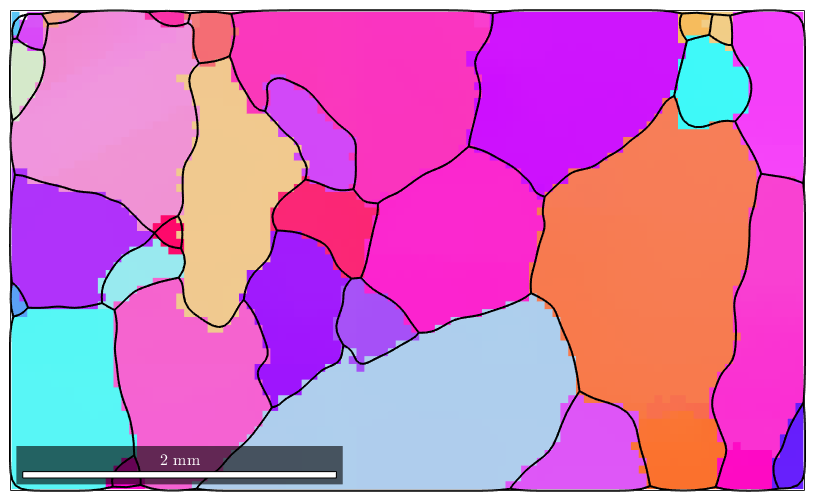
close all; plotx2east mtexdata forsterite ebsd = ebsd(inpolygon(ebsd,[10 4 5 3]*10^3)); plot(ebsd('Fo'),ebsd('Fo').orientations) hold on plot(ebsd('En'),ebsd('En').orientations) plot(ebsd('Di'),ebsd('Di').orientations) % compute grains [grains,ebsd.grainId] = calcGrains(ebsd('indexed'),'angle',10*degree); % remove small grains ebsd(grains(grains.grainSize < 3)) = []; % and repeat the grain computation [grains,ebsd.grainId] = calcGrains(ebsd('indexed'),'angle',10*degree); % grains = smooth(grains,5); % plot the boundary of all grains plot(grains.boundary,'linewidth',2) hold off
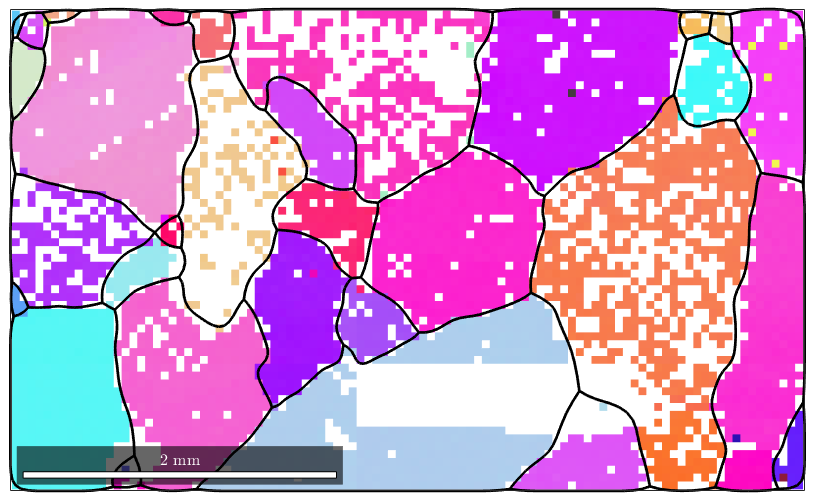
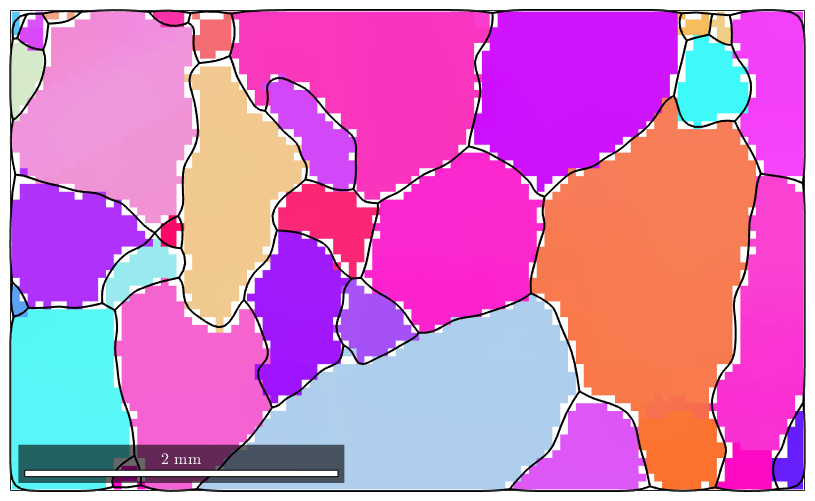
Using the option fill the command smooth fills the holes inside the grains. Note that the nonindexed pixels at the grain boundaries kept untouched. In order to allow MTEX to decide whether a pixel is inside a grain or not, the grain variable has to be passed as an additional argument.
F = halfQuadraticFilter; F.alpha = 0.01; F.eps = 0.001; ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd('indexed'),F,'fill',grains); plot(ebsd_smoothed('Fo'),ebsd_smoothed('Fo').orientations) hold on plot(ebsd_smoothed('En'),ebsd_smoothed('En').orientations) plot(ebsd_smoothed('Di'),ebsd_smoothed('Di').orientations) % plot the boundary of all grains plot(grains.boundary,'linewidth',1.5) % stop overide mode hold off
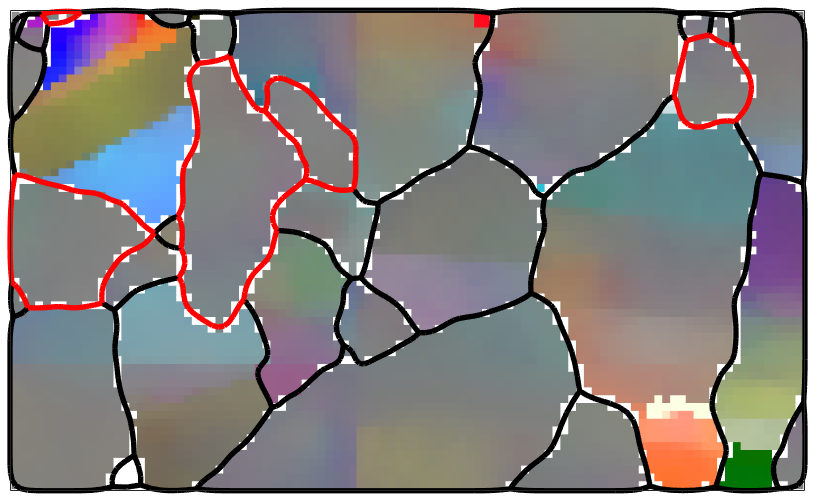
In order to visualize the orientation gradient within the grains, we plot the misorientation to the meanorientation. We observe that the mis2mean varies smoothly also within the regions of not indexed orientations.
% plot mis2mean for all phases ipfKey = axisAngleColorKey(ebsd_smoothed('Fo')); ipfKey.oriRef = grains(ebsd_smoothed('fo').grainId).meanOrientation; ipfKey.maxAngle = 2.5*degree; color = ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('Fo').orientations); plot(ebsd_smoothed('Fo'),color,'micronbar','off') hold on ipfKey.oriRef = grains(ebsd_smoothed('En').grainId).meanOrientation; plot(ebsd_smoothed('En'),ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd_smoothed('En').orientations)) % plot boundary plot(grains.boundary,'linewidth',4) plot(grains('En').boundary,'lineWidth',4,'lineColor','r') hold off
For comparison
ipfKey.oriRef = grains(ebsd('fo').grainId).meanOrientation; ipfKey.maxAngle = 2.5*degree; color = ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd('Fo').orientations); plot(ebsd('Fo'),color,'micronbar','off') hold on ipfKey.oriRef = grains(ebsd('En').grainId).meanOrientation; plot(ebsd('En'),ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd('En').orientations)) % plot boundary plot(grains.boundary,'linewidth',4) plot(grains('En').boundary,'lineWidth',4,'lineColor','r') hold off
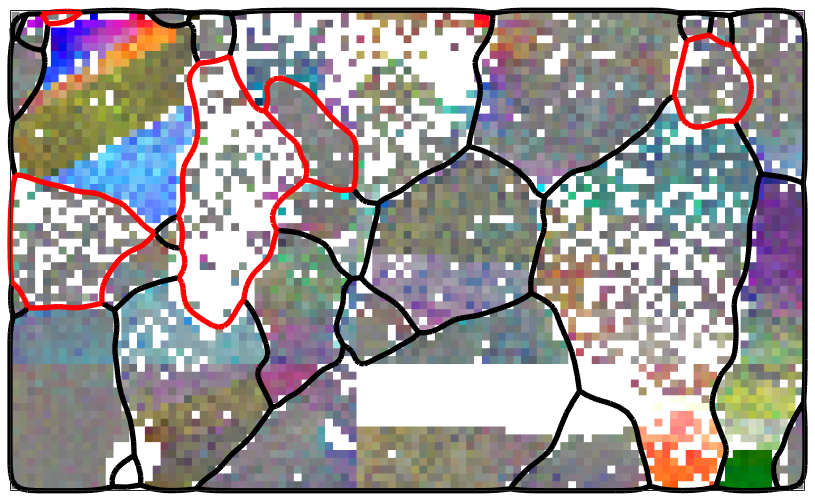
If no grain variable is passed to the smoothing command the not indexed pixels are assigned to the nearest neighbor.
ebsd_smoothed = smooth(ebsd('indexed'),F,'fill'); plot(ebsd_smoothed('Fo'),ebsd_smoothed('Fo').orientations) hold on plot(ebsd_smoothed('En'),ebsd_smoothed('En').orientations) plot(ebsd_smoothed('Di'),ebsd_smoothed('Di').orientations) % plot the boundary of all grains plot(grains.boundary,'linewidth',1.5) % stop overide mode hold off
| DocHelp 0.1 beta |